The Mediterranean diet— if it is even a “diet” in a traditional sense — is a model of eating that has become one of the world’s most delicious and healthiest eating plans. Based on the healthy diets of people living in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, this plan includes a variety of delicious chicken, fish, beef, and vegetable dishes, which feature foods like fruits, veggies, whole grains, and healthy fats.
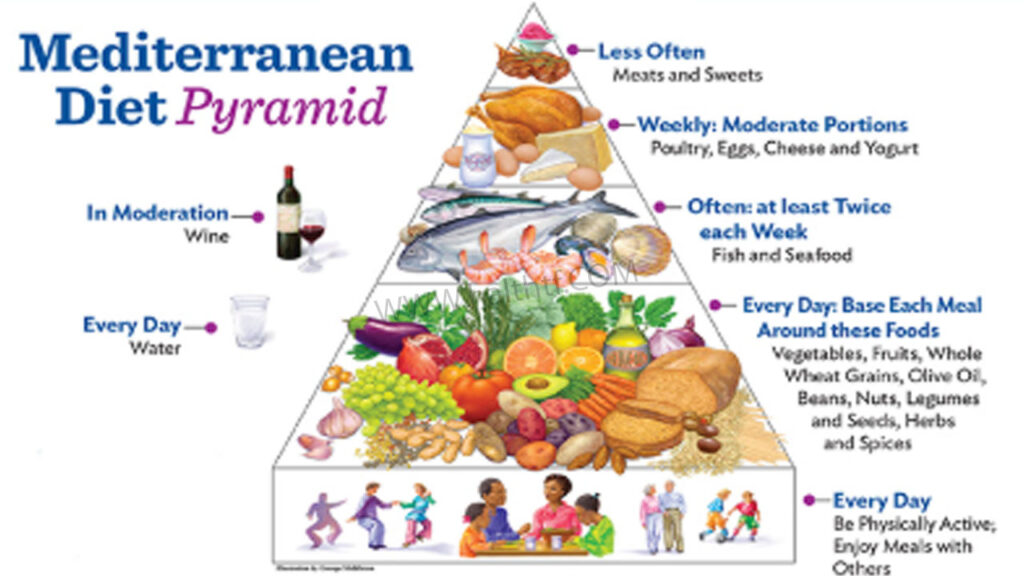
At its heart, the Mediterranean diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds—all foods that are full of fiber, vitamins and anioxidants. Olive oil is the main and only healthy fat as butter/margarine are eliminated altogether, and is generously used in cooking and salads. Fish and seafood are recommended several times a week, and poultry, eggs, and other dairy products are eaten in moderation. This includes only allowing red meat and sweets on an ad hoc basis.
They season with herbs, garlic, lemon and spices and not heavy salt. One of the benefits of this as a diet it tastes great. With no processed foods, it’s also naturally lower in sodium, which is good for the heart. So that, in moderate consumption of it red wine is an old tradition in some followers.
Research repeatedly indicates that the Mediterranean diet lowers the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and obesity, in addition to encouraging a balanced and pleasurable way of eating.
The DASH Diet
The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is a well-researched eating plan that’s been proven to lower blood pressure and support heart health. It is also low in sodium and includes nutrient dense foods that offer essential vitamins and minerals,thus is ideal for people with or at risk of hypertension and heart disease.
The building blocks of the DASH diet are fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. These foods contain potassium, magnesium, calcium and fiber -four key components that help control blood pressure. Lean meats, fish, poultry, beans and nuts provide protein, while red meats, processed foods and added sugars are limited.
Sodium is one the most important concepts in the DASH diet. Sodium intake is reduced to 1,500 to 2,300 mg per day, according to individual health requirements – far below the modern average. Herbs, spices, lemon and garlic are added to dishes rather than salt, resulting in flavorful and heart-healthy fare.
The DASH diet has been shown to reduce blood pressure and the risk of stroke, type 2 diabetes and kidney disease. It focuses on lifelong health and flexibility and variety in meals.
Plant-based and flexitarian diets
A plant-based diet focuses on foods that mostly come from plants, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. Though some versions represent a total assiduousness to not eating animals, other vegans might allow small amounts of fish, meat or dairy in their diets on occasion. This diet packs plenty of fiber, antioxidants and healthy fat, which can help reduce your risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes and obesity, while also improving digestion and weight management.

Or the flexitarian diet, a more flexible form of plant-based eating. Instead of banning all meat, it promotes plant-based meals most of the time, with lean meat, poultry and fish a couple times a week. This makes it simpler to ease into a healthier way of life without food limitations. It’s perfect for folks who are eager for the benefits of plant-based nutrition but who don’t mind consuming some animal products in moderation.
Both are based on a few simple principles: eat whole foods that are not overly processed; minimize added sugar and salt; and prioritize nutrient-dense offerings. They are also environmentally sustainable as they reduce the dependence on resource-intensive meat production.
Through incorporating a plant-based or flexitarian approach, people can feel healthier, more energized, and stay grounded in practical ways that are sustainable and delicious for the long haul.
The MIND Diet
What is the MIND diet? The MIND diet (which stands for Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay) is a hybrid of two established diet plans (the Mediterranean diet and DASH diet) and is the first of its kind to introduce components of each diet that focus on brain health and preventing Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
This diet focuses on the foods that have been found to have a positive impact on your cognitive skills. Key ingredients include nutrient-dense leafy greens like spinach and kale, other vegetables for variety, and vitamins and antioxidants. Berries, in particular blueberries and strawberries, are singled out for their potent brain-protective compounds. Whole grains, beans, nuts, olive oil, and fish are recommended as staples, while you’re OK to eat moderate amounts of poultry and (optional) wine.
The MIND diet discourages the consumption of red meat, butter, cheese, sweets, fried foods and fast food, as these have been associated with inflammation and cognitive decline. Compared to some stricter eating plans, it puts more emphasis on consistency rather than perfection — which makes it a more sustainable plan over the long term.
People who adhere closely to the MIND diet may lower their risk of Alzheimer’s disease by as much as 53 percent, and cognitive decline overall by 35 percent, according to a study published in the #12 Heart Disease Research and #14 Alzheimer’s journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia. Just some moderate following of the diet has been linked to brain-health benefits, making MIND a realistic and fairly easy to follow way to feed both your body and your brain.
WW (formerly Weight Watchers)
WW, the new Weight Watchers, is a global wellness company that takes a people-first approach to products, programs and experiences that inspire and guide people to reach their goals. Rather than restrictive dieting, WW encourages healthy eating, behavior modification, physical activity, and rediscovering your mindset when it comes to eating and dieting for long term health and lasting weight loss.
Central to the WW program: its SmartPoints system, which tallies up point values based on the calories, protein, sugar and saturated fat in foods and drinks. Whole, healthy foods, like fruits, vegetables and lean proteins, have zero or low point values, which incentivize members to make good choices and not feel deprived. It gives members a personalized daily and weekly SmartPoints budget for flexibility and freedom when meal planning.
WW also offers ZeroPoint foods (like eggs, legumes, non-starchy vegetables and plain yogurt) that you don’t need to track. Participants can eat meals consisting of healthy staples, with regular treats.
In addition to food, WW promotes holistic wellness by providing exercise tracking, sleep management and mindfulness tools through its app and digital community. It’s an amazing program because it is easy for any lifestyle, one of the most convenient and sustainable approaches to a healthy lifestyle.
Intermittent Fasting: A Simple Approach to Better Health
Intermittent fasting (IF), a popular eating pattern, emphasizes when you eat instead of what you eat. It’s basically moving through periods of eating and fasting to give our bodies a rest and time to heal. While restrictive in some aspects, a flexible approach to eating is really what makes the “Intermittent” in intermittent fasting more about when to eat as opposed to what to eat.
One of the most popular is what’s become known as the 16/8 method, which means doing a 16-hour fast and eating only within an 8-hour window. It could look something like eating between noon and 8 p.m., then not eating from 8 p.m. until noon the next day. Other forms of the diet include the 5:2 diet, in which you eat as you normally would five days a week, then eat very little — like fewer than 600 calories — two non-consecutive days a week.
Studies show intermittent fasting can help with weight control, improved metabolism, better blood sugar control, possibly better cellular repair. Others say they have more energy, focus and mental clarity.
However, beginners should start gradually. Start with a 12 hour fast and increase the window as your body adjust. It’s equally important to concentrate on healthy, balanced meals during eating times — lean proteins, whole grains, vegetables, healthy fats.
Intermittent fasting isn’t for everyone. People with medical issues, pregnant women or those with eating disorders should first consult a doctor.
When done consistently, intermittent fasting is a sustainable means to maintain lifelong health.
The Volumetrics Diet: Eating More, Weighing Less
Developed by nutrition researcher Dr. Barbara Rolls, the Volumetrics Diet is an eating plan that helps you lose weight without feeling like you’re on a diet. Rather than severely restricted, this diet emphasizes eating more of the foods that are low in calories but high in volume, such as fruits, vegetables, soups, and whole grains.
The basic concept is calorie density — the number of calories a food contains relative to its weight or volume. Low-calorie-dense foods — such as strawberries or leafy greens — satisfy your hunger without contributing too many calories. On the flip side, high-calorie foods like fried snacks, dessert and fatty meats should be restricted as well.
The eating pattern categorized foods into four groups:
Ultra-low-density (fruit, non-starchy vegetables, broth-based soups)
Low-starch (whole grains, lean protein, beans)
Medium-density (cheese, bread, desserts)
High-density (fried foods, candies, oils)
“If you mostly choose the types of Category 1 and 2 foods, you’re able to eat satisfying portions and still be in a calorie deficit,” Grupski says. The program also promotes regular exercise and conscientious consumption.
Because the Volumetrics Diet doesn’t eliminate food groups, it is considered sustainable and flexible. Rather, it teaches people how to eat smarter, feel fuller and live a more intentional life that’s mindful — even when that means letting go and savoring a diverse range of foods.
The Mayo Clinic Diet: A Lifestyle Approach to Healthy Living
The Mayo Clinic Diet is a science-based weight loss program that will guide you to a healthier life. A program created by specialists at the Mayo Clinic, it concentrates on eating healthy foods, adding in physical activity and adopting small and realistic lifestyle changes.
The program has two phases. The first phase, “Lose It!”, runs for two weeks and focuses on breaking old habits while getting weight loss started. At this stage, participants include healthful habits such as eating breakfast daily, exercising for 30 minutes or more and restricting added sugar. Unhealthy behaviors like snacking on highly processed foods or snacking while watching television are replaced with better ones.
The second phase, “Live It!”, is a sustained approach that can keep weight off. It offers new dietary guidelines that substitute the Mayo Clinic’s emphasis on the food pyramid with its own guide — the Mayo Clinic Healthy Weight Pyramid — which is based on filling most of your plate with fruits, vegetables and whole grains, and eating lean protein and healthy fat in moderation. There are no off-limits foods, and sweets and high-calorie snacks are ok — in moderation — to make the diet realistic and flexible.
Though it takes longer to see results than fad diets, the Mayo Clinic Diet prioritizes balance, moderation, and lifestyle change over those quick fixes. It helps maintaining weight and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases which are responsible for global deaths, promoting good health and well being.
Low-Carb Diets: A Popular Path to Weight Loss and Health
Low-carb diets center on limiting carbohydrate consumption, including bread, pasta, rice, and sugary foods, and prioritizing proteins, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables. With reduced carb intake, the body utilizes stored fat for energy which can also provide a source of energy and lead to weight loss.
Several kinds of low-carb diets. The ketogenic (keto) diet is the most strict of the low-carb diets, allowing only 5% of carbs and forcing the body into a state of ketosis, where fat becomes the main fuel source. Moderate plans, like the Atkins or South Beach diet, introduce some whole grains, fruits and legumes following the initial stages.
Reduced insulin levels also make your kidneys shed excess sodium, leading to immediate weight loss, and quick reduction of water weight.” Benefits of Low Carb Diets: Better Blood Sugar Control Lower Cravings Healthier Cholesterol Levels Faster Weight Loss Than Low Fat Diets It’s common for individuals to have more energy and not get hungry as often because of the focus on protein and fat.
But low-carb diets are not for everyone. Others may suffer side effects such as fatigue, headache or nutrient deficiencies if not properly balanced. It is essential to select whole, nutrient-dense foods, and to consult a health care provider before altering your diet in a significant way.
When done the right way, a low-carb diet can be a sustainable and incredibly healthy way to lose body fat and improve metabolic health.


